WATER TREATMENT
SEDIMENT FILTRATION
Sediment filtration cleans water from slime and mechanical contaminants (e.g. sand or rust). It is often the first and most essential stage of filtration. It may be carried out on a special filtration bed (e.g. AG Plus) or by means of cartridge filters that can remove mechanical contaminants about the size of 1-1oo microns – filter housings, Cintropur filters.
ACTIVATED CARBON FILTRATION
Activated carbon represents adsorption properties for many compounds such as: chlorine, phenols, organic compounds of humus and organochloride origin, which is completely safe for people and natural environment. Activated carbon improves the taste and smell of water and is widely used in production processes (fat, oil, alcohol treatment) and as a part of whole house water treatment.
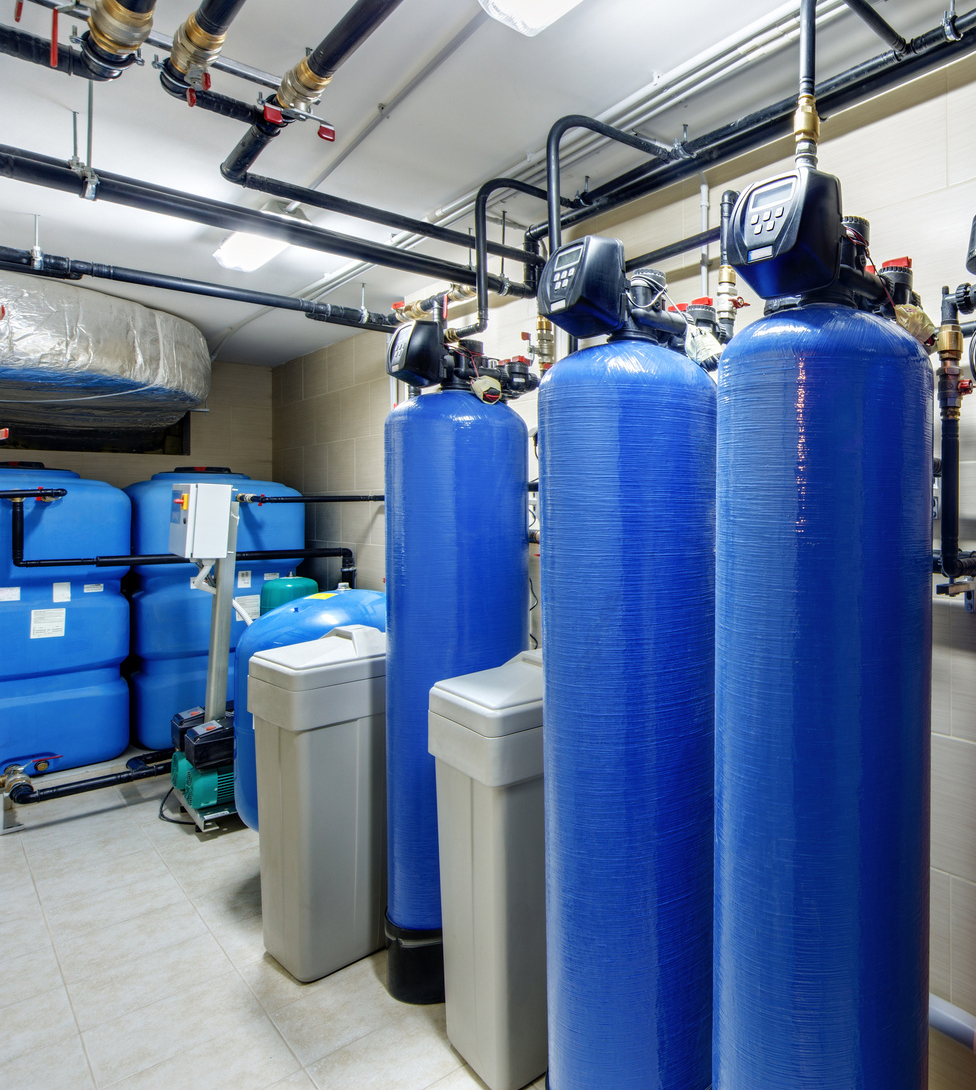
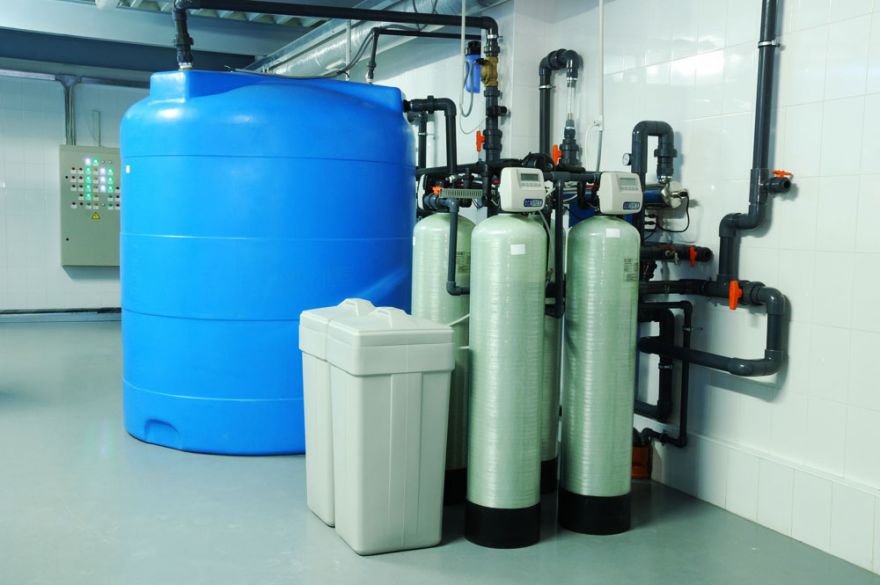
WATER SOFTENING
Water softening is a process based on ion exchange. Calcium and magnesium ions, responsible for water hardness, are traced during the water flow through an ion exchange resin. After time, a filter bed (ion exchange resin) becomes exhausted and needs regeneration by rinsing in a solution of brine and water. During the regeneration process, retained calcium and magnesium ions are removed to the sewage system and the filter bed gains its initial exchange capacity.
IRON AND MANGANESE REMOVAL
The presence of iron and manganese compounds in water is a serious problem when using the water for industrial purposes. The removal of soluble iron compounds (in the form of divalent iron ions) is based on their conversion into insoluble compounds (in the form of trivalent iron ions) which are easy to erase in the filtration process on a proper filter bed. Similarly, manganese compounds are removed by oxidizing divalent manganese to a tetravalent form.
Iron and manganese removal technologies are widely used in the food and processing industry, heating, brewing and community water treatment plants.